Ancient Greece for Dummies

 Achilles killing the Amazon Queen Penthesilea, 540-530 B.C.E., black-figured amphora (wine-jar), signed by Exekias as potter and attributed to him as painter, 46 cm tall, Athens, Greece © Trustees of the British Museum. Penthesilea brought her Amazon warriors to help the Trojans defend their city, but was killed in combat with Achilles, the greatest of the Greek warriors.
Achilles killing the Amazon Queen Penthesilea, 540-530 B.C.E., black-figured amphora (wine-jar), signed by Exekias as potter and attributed to him as painter, 46 cm tall, Athens, Greece © Trustees of the British Museum. Penthesilea brought her Amazon warriors to help the Trojans defend their city, but was killed in combat with Achilles, the greatest of the Greek warriors.
The ancient Greeks lived in many lands around the Mediterranean Sea, from Turkey to the south of France. They had close contacts with other peoples such as the Egyptians, Syrians and Persians.The Greeks lived in separate city-states, but shared the same language and religious beliefs.
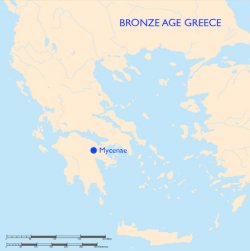 Bronze Age Greece
Bronze Age Greece
During the Bronze Age (around 3200 – 1100 B.C.E.), a number of cultures flourished on the islands of the Cyclades, in Crete and on the Greek mainland. They were mainly farmers, but trade across the sea, particularly in raw materials such as obsidian (volcanic glass) and metals, was growing.
Mycenaean culture flourished on the Greek mainland in the Late Bronze Age, from about 1600 to 1100 B.C.E. The name comes from the site of Mycenae, where the culture was first recognized after the excavations in 1876 of Heinrich Schliemann.
Pottery stemmed bowl decorated with a procession of riders in chariots, Mycenaean, about 1400-1300 B.C.E., 42 cm high, Cyprus, Greece
© Trustees of the British Museum. The upper zone of the vase is painted with a frieze of chariots, pulled by elongated horses, in which ride a charioteer and a passenger. Such chariot processions on vases may well have been inspired by contemporary fresco-paintings which decorated the walls of Mycenaean palaces.
Such chariot processions on vases may well have been inspired by contemporary fresco-paintings which decorated the walls of Mycenaean palaces.
The Mycenaean period of the later Greek Bronze Age was viewed by the Greeks as the "age of heroes" and perhaps provides the historical background to many of the stories told in later Greek mythology, including Homer's epics. Objects and artworks from this time are found throughout mainland Greece and the Greek islands. Distinctive Mycenaean pottery was distributed widely across the eastern Mediterranean. These show the beginnings of Greek mythology being used to decorate works of art. They come from about the same time that the epics of Homer were reaching the form in which we inherit them, as the earliest Greek literature.
The collapse of Mycenaean civilization around 1100 B.C.E. brought about a period of isolation known as the Dark Age. But by around 800 B.C.E. the revival had begun as trade with the wider world increased, arts, crafts and writing re-emerged and city-states (poleis) developed.
The Strangford Apollo, c. 500-490 B.C.E., 101 cm high, perhaps from Cyclades, Aegean Sea
© Trustees of the British MuseumArchaic period
Two of the most distinctive forms of free-standing sculpture to emerge during the Archaic period of Greek art (about 600-480 B.C.E.) were statues of youths (kouroi) and maidens (korai).


|
World's Great Men of Color, Volume I: Asia and Africa, and Historical Figures Before Christ, Including Aesop, Hannibal, Cleopatra, Zenobia, Askia the Great, and Many Others Book (Touchstone)
|
|

|
Photo Jigsaw Puzzle of The ruins of ancient Delphi, UNESCO World Heritage Site, Greece, Europe Home (robertharding)
|